關于Java HashMap自動排序的簡單剖析
1.HashMap概述
HashMap是無序的,這里無序的意思是你取出數(shù)據(jù)的順序與你存入數(shù)據(jù)的順序不同
2.發(fā)現(xiàn)問題
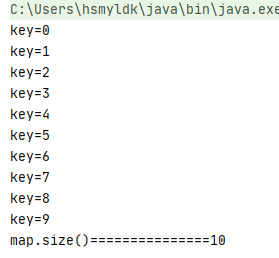
當嘗試向HashMap中存入int類型的key,可以看到在輸出的時候會自動排序
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(3, 'asdf'); map.put(2, 'asdf'); map.put(1, 'asdf'); map.put(6, 'asdf'); map.put(5, 'asdf'); map.put(4, 'asdf'); map.put(8, 'asdf'); map.put(9, 'asdf'); map.put(7, 'asdf'); map.put(0, 'asdf');
輸出
3.實現(xiàn)原理
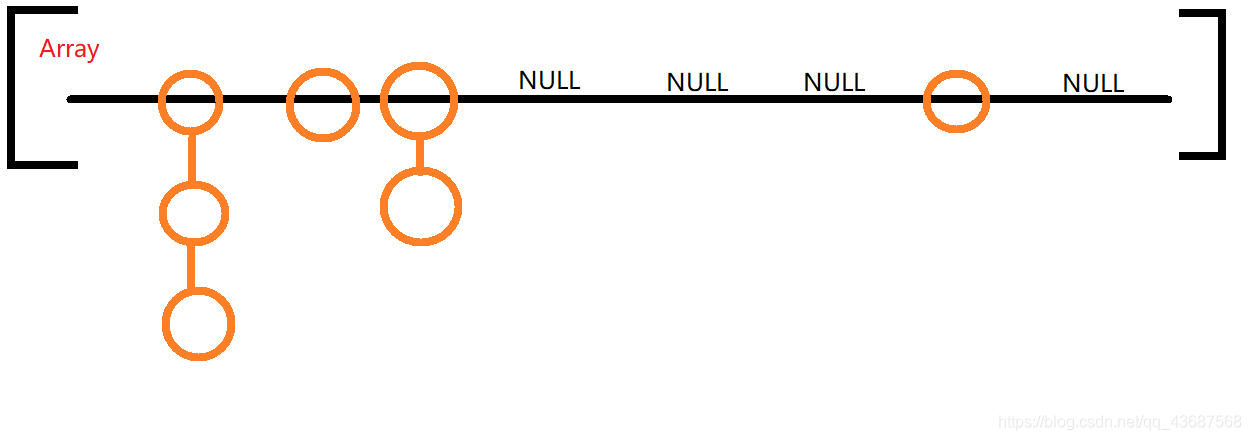
我們都知道,HashMap是數(shù)組加鏈表實現(xiàn)的,在鏈表長度大于8的時候將鏈表轉化為紅黑樹數(shù)組加鏈表畫一下模型圖是這樣的,黑色的是數(shù)組,橙色的是鏈表,遍歷HashMap的key的時候,先遍歷第一列,然后第二列。。。
4.翻看源碼
HashMap的默認數(shù)組長度為16,默認負載因子是0.75,意思就是當數(shù)組內不為null的元素大于(數(shù)組長度*負載因子)的時候就會拓容數(shù)組
如果數(shù)組長度和負載因子都是默認值,那當在數(shù)組中存入第13個元素后就會拓容16*0.75=12
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
再讀一下put方法和hash方法
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } //獲取key的hash,當key為int類型的時候hash=key的值 static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; //tab就是HashMap的數(shù)組,這句話就是初始化數(shù)組 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; //如果根據(jù)hash值來判斷將此元素放在什么位置,如果數(shù)組當前位置 //為空直接存放,成為一個長度為一的鏈表 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//================== tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //如果不是,則將當前元素放在當前位置下元素的后邊形成鏈表 else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) //拓容數(shù)組 resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
5.分析
17行:if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
(n - 1) & hash
n-1就是數(shù)組的length-1,現(xiàn)在數(shù)組長度是16,
15&hash,
例如,現(xiàn)在存入key為1,
15轉成二進制為1111
1 轉成二進制為0001,
所以i=15&1=1;
現(xiàn)在1就存放在數(shù)組下標為1的位置
如果放2,那就放在數(shù)組下標為2的位置,
如果再存放17的話,
1501111
1710001
15&17=1;因為數(shù)組下標1的位置有上一次存放的key為1的元素,所以就將key=17的元素掛在key=1的下邊,
這是遍歷HashMap的key就會變成1,17,2
順序就會亂掉,現(xiàn)在數(shù)組的長度是16,已使用的是2,還沒有達到拓容那一步,
6.驗證
下邊的代碼是存放11個數(shù)據(jù),拓容要存入第13個數(shù)據(jù)時進行拓容
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(3, 'asdf'); map.put(2, 'asdf'); map.put(1, 'asdf'); map.put(6, 'asdf'); map.put(5, 'asdf'); map.put(4, 'asdf'); map.put(8, 'asdf'); map.put(9, 'asdf'); map.put(7, 'asdf'); map.put(0, 'asdf'); map.put(17,'saf');// map.put(10,'saf');// map.put(11,'saf'); for (int i : map.keySet()) { System.out.println('key=' + i); } System.out.println('map.size()===============' + map.size());
下邊這段代碼的輸出結果就是
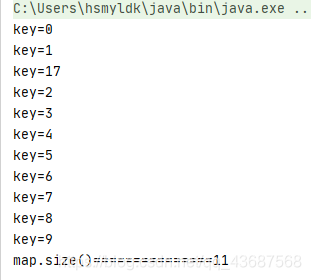
和分析的一樣,
如果再添加兩個數(shù)據(jù),使其拓容
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(3, 'asdf'); map.put(2, 'asdf'); map.put(1, 'asdf'); map.put(6, 'asdf'); map.put(5, 'asdf'); map.put(4, 'asdf'); map.put(8, 'asdf'); map.put(9, 'asdf'); map.put(7, 'asdf'); map.put(0, 'asdf'); map.put(17,'saf');// map.put(10,'saf');// map.put(11,'saf'); for (int i : map.keySet()) { System.out.println('key=' + i); } System.out.println('map.size()===============' + map.size());
輸出是
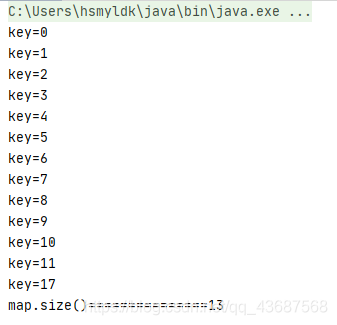
又排好了順序
7.結論
當所有key的hash的最大值<數(shù)組的長度-1時HashMap可以將存入的元素按照key的hash從小到大排序不過這個發(fā)現(xiàn)沒有什么用就是了,不過看了一天源碼收獲不少,還看到好幾種沒見過的寫法
到此這篇關于關于Java HashMap自動排序簡單剖析的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Java HashMap自動排序內容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關文章:
1. .Net加密神器Eazfuscator.NET?2023.2?最新版使用教程2. 詳解瀏覽器的緩存機制3. Xml簡介_動力節(jié)點Java學院整理4. python多線程和多進程關系詳解5. 一款功能強大的markdown編輯器tui.editor使用示例詳解6. Python xlrd/xlwt 創(chuàng)建excel文件及常用操作7. python 寫函數(shù)在一定條件下需要調用自身時的寫法說明8. 存儲于xml中需要的HTML轉義代碼9. Python 實現(xiàn)勞拉游戲的實例代碼(四連環(huán)、重力四子棋)10. ASP動態(tài)網(wǎng)頁制作技術經(jīng)驗分享
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備