解讀Oracle中代替like進行模糊查詢的方法instr(更高效)
目錄
- 一、簡介
- 二、使用說明
- 對應參數描述
- 我們以一些示例講解使用方法
- 三、instr()與like比較
- instr函數也有三種情況
- 下面通過一個示例說明like 與 instr()的使用比較
- 四、效率對比
- 五、總結
一、簡介
相信大家都使用過like進行模糊匹配查詢,在oracle中,instr()方法可以用來代替like進行模糊查詢,大數據量的時候效率更高。
本文將對instr()的基本使用方法進行詳解以及通過示例講解與like的效率對比。
二、使用說明
instr(sourceString,destString,start,appearPosition) ? ??
對應參數描述
instr('源字符串' , '目標字符串' ,'開始位置','第幾次出現'),返回目標字符串在源字符串中的位置。
后面兩個參數可要可不要。
我們以一些示例講解使用方法
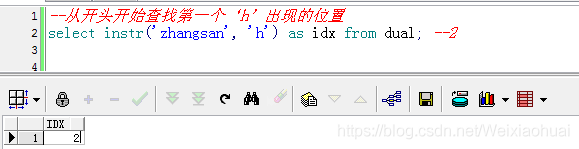
【a】從開頭開始查找第一個‘h’出現的位置
--從開頭開始查找第一個‘h"出現的位置select instr("zhangsan", "h") as idx from dual; --2查詢結果:
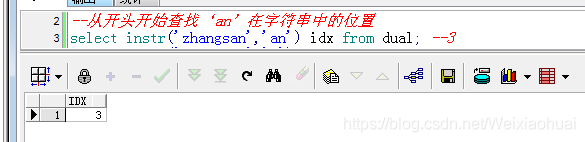
【b】從開頭開始查找‘an’在字符串中的位置
--從開頭開始查找‘an"在字符串中的位置select instr("zhangsan","an") idx from dual; --3查詢結果:
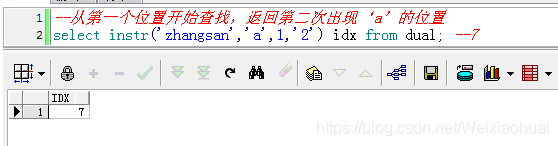
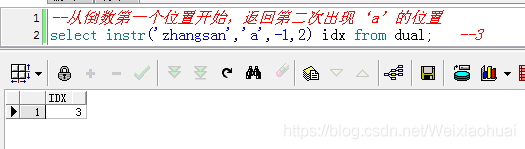
【c】從第一個位置開始查找,返回第二次出現‘a’的位置
--從第一個位置開始查找,返回第二次出現‘a"的位置select instr("zhangsan","a",1,"2") idx from dual; --7查詢結果:
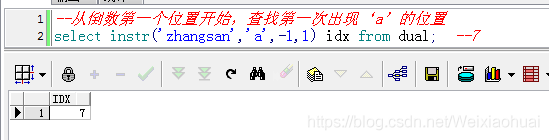
【d】從倒數第一個位置開始,查找第一次出現‘a’的位置
--從倒數第一個位置開始,查找第一次出現‘a"的位置select instr("zhangsan","a",-1,1) idx from dual; --7查詢結果:
【e】從倒數第一個位置開始,返回第二次出現‘a’的位置
--從倒數第一個位置開始,返回第二次出現‘a"的位置select instr("zhangsan","a",-1,2) idx from dual; --3查詢結果:
三、instr()與like比較
instr函數也有三種情況
- a. instr(字段,'關鍵字') > 0 相當于 字段like '%關鍵字%': 表示在字符串中包含‘關鍵字’
- b. instr(字段,'關鍵字') = 1 相當于 字段like '關鍵字%' 表示以‘關鍵字’開頭的字符串
- c. instr(字段,'關鍵字') = 0 相當于 字段not like '%關鍵字%' 表示在字符串中不包含‘關鍵字’
下面通過一個示例說明like 與 instr()的使用比較
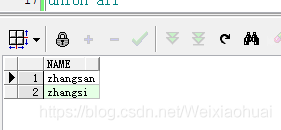
【a】使用like進行模糊查詢
with temp1 as (select "zhangsan" as name from dual),temp2 as (select "zhangsi" as name from dual),temp3 as (select "xiaoming" as name from dual),temp4 as (select "xiaohong" as name from dual),temp5 as (select "zhaoliu" as name from dual) select * from (select * from temp1 union allselect * from temp2union allselect * from temp3union allselect * from temp4union all select * from temp5) res where res.name like "%zhang%"
查詢字符串中包含‘zhang’的結果:
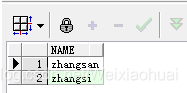
【b】使用instr()進行模糊查詢
(1) 查詢字符串中包含‘zhang’的結果:
with temp1 as (select "zhangsan" as name from dual),temp2 as (select "zhangsi" as name from dual),temp3 as (select "xiaoming" as name from dual),temp4 as (select "xiaohong" as name from dual),temp5 as (select "zhaoliu" as name from dual) select * from (select * from temp1 union allselect * from temp2union allselect * from temp3union allselect * from temp4union all select * from temp5) res where instr(res.name,"zhang") > 0;
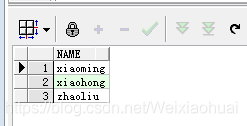
(2) 查詢字符串中不包含‘zhang’的結果:
with temp1 as (select "zhangsan" as name from dual),temp2 as (select "zhangsi" as name from dual),temp3 as (select "xiaoming" as name from dual),temp4 as (select "xiaohong" as name from dual),temp5 as (select "zhaoliu" as name from dual) select * from (select * from temp1 union allselect * from temp2union allselect * from temp3union allselect * from temp4union all select * from temp5) res where instr(res.name,"zhang") = 0;
(3) 查詢以‘zhang’開頭的字符串:
with temp1 as (select "zhangsan" as name from dual),temp2 as (select "zhangsi" as name from dual),temp3 as (select "sizhangsan" as name from dual),temp4 as (select "xiaohong" as name from dual),temp5 as (select "zhaoliu" as name from dual) select * from (select * from temp1 union allselect * from temp2union allselect * from temp3union allselect * from temp4union all select * from temp5) res where instr(res.name,"zhang") = 1;
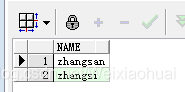
(4)instr與like特殊用法
select id, name from users where instr("a, b", id) > 0;--等價于select id, name from users where id = a or id = b;--等價于select id, name from users where id in (a, b);四、效率對比
【a】使用plsql創建一張十萬條數據測試數據表,同時為需要進行模糊查詢的列增加索引
--創建10萬條測試數據create table test_instr_like as select rownum as id,"zhangsan" as name from dualconnect by level <= 100000; --name列建立索引create index idx_tb_name on test_instr_like(name);
【b】使用like進行模糊查詢
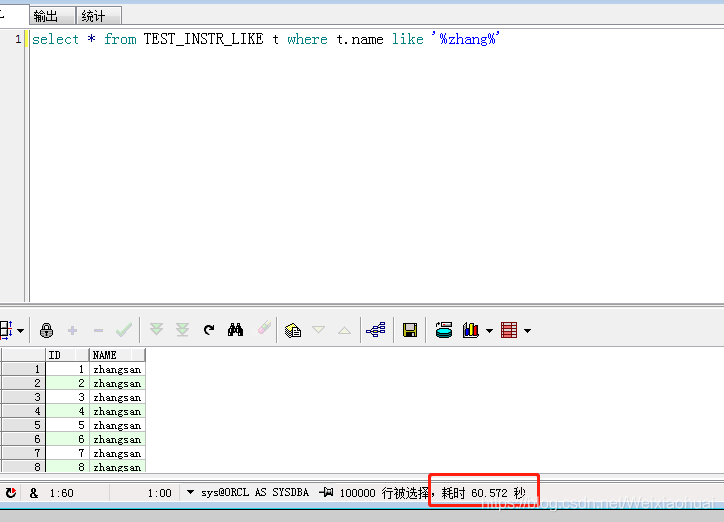
select * from TEST_INSTR_LIKE t where t.name like "%zhang%"
總耗時: 60秒
【c】使用instr進行模糊查詢
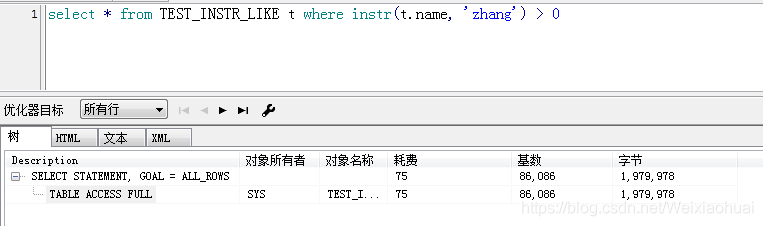
select * from TEST_INSTR_LIKE t where instr(t.name, "zhang") > 0;
總耗時:50秒
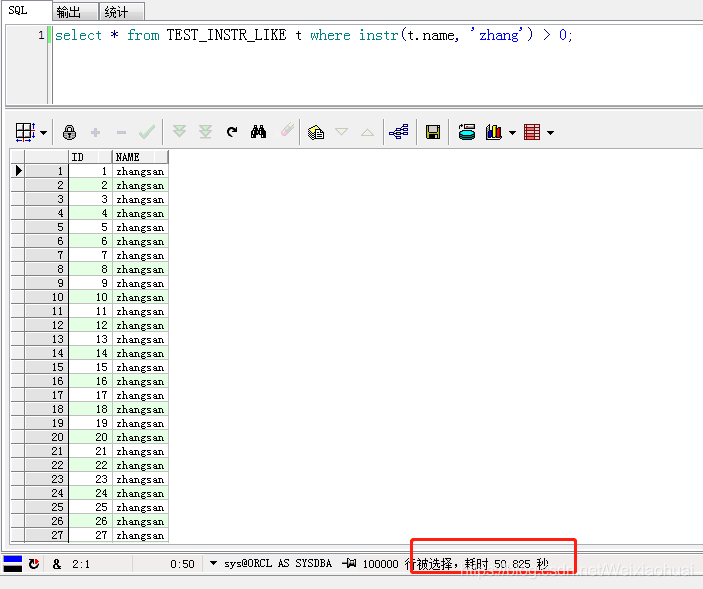
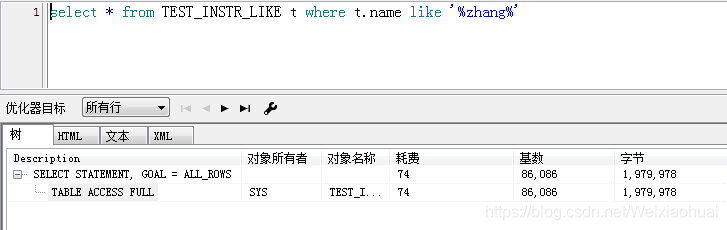
由圖可見,instr查詢的速度確實比like快一些,但是,看執行計劃的話,instr卻比like耗時一點。如下圖:
五、總結
以上是對instr基本使用方法的講解以及通過示例對比了like與instr的效率,在進行模糊查詢的時候,能用instr的話就盡量用instr,畢竟數據量大的時候還是有一點優勢的,本文是筆者對like以及instr的一些總結和見解,僅供大家學習參考,也希望大家多多支持。
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備