python使用梯度下降算法實現一個多線性回歸
python使用梯度下降算法實現一個多線性回歸,供大家參考,具體內容如下
圖示:


import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pylab as pltimport numpy as np# Read data from csvpga = pd.read_csv('D:python3dataTest.csv')# Normalize the data 歸一化值 (x - mean) / (std)pga.AT = (pga.AT - pga.AT.mean()) / pga.AT.std()pga.V = (pga.V - pga.V.mean()) / pga.V.std()pga.AP = (pga.AP - pga.AP.mean()) / pga.AP.std()pga.RH = (pga.RH - pga.RH.mean()) / pga.RH.std()pga.PE = (pga.PE - pga.PE.mean()) / pga.PE.std()def cost(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y): # Initialize cost J = 0 # The number of observations m = len(x1) # Loop through each observation # 通過每次觀察進行循環 for i in range(m): # Compute the hypothesis # 計算假設 h=theta0+x1[i]*theta1+x2[i]*theta2+x3[i]*theta3+x4[i]*theta4 # Add to cost J += (h - y[i])**2 # Average and normalize cost J /= (2*m) return J# The cost for theta0=0 and theta1=1def partial_cost_theta4(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,x1,x2,x3,x4,y): h = theta0 + x1 * theta1 + x2 * theta2 + x3 * theta3 + x4 * theta4 diff = (h - y) * x4 partial = diff.sum() / (x2.shape[0]) return partialdef partial_cost_theta3(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,x1,x2,x3,x4,y): h = theta0 + x1 * theta1 + x2 * theta2 + x3 * theta3 + x4 * theta4 diff = (h - y) * x3 partial = diff.sum() / (x2.shape[0]) return partialdef partial_cost_theta2(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,x1,x2,x3,x4,y): h = theta0 + x1 * theta1 + x2 * theta2 + x3 * theta3 + x4 * theta4 diff = (h - y) * x2 partial = diff.sum() / (x2.shape[0]) return partialdef partial_cost_theta1(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,x1,x2,x3,x4,y): h = theta0 + x1 * theta1 + x2 * theta2 + x3 * theta3 + x4 * theta4 diff = (h - y) * x1 partial = diff.sum() / (x2.shape[0]) return partial# 對theta0 進行求導# Partial derivative of cost in terms of theta0def partial_cost_theta0(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y): h = theta0 + x1 * theta1 + x2 * theta2 + x3 * theta3 + x4 * theta4 diff = (h - y) partial = diff.sum() / (x2.shape[0]) return partialdef gradient_descent(x1,x2,x3,x4,y, alpha=0.1, theta0=0, theta1=0,theta2=0,theta3=0,theta4=0): max_epochs = 1000 # Maximum number of iterations 最大迭代次數 counter = 0 # Intialize a counter 當前第幾次 c = cost(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) ## Initial cost 當前代價函數 costs = [c] # Lets store each update 每次損失值都記錄下來 # Set a convergence threshold to find where the cost function in minimized # When the difference between the previous cost and current cost # is less than this value we will say the parameters converged # 設置一個收斂的閾值 (兩次迭代目標函數值相差沒有相差多少,就可以停止了) convergence_thres = 0.000001 cprev = c + 10 theta0s = [theta0] theta1s = [theta1] theta2s = [theta2] theta3s = [theta3] theta4s = [theta4] # When the costs converge or we hit a large number of iterations will we stop updating # 兩次間隔迭代目標函數值相差沒有相差多少(說明可以停止了) while (np.abs(cprev - c) > convergence_thres) and (counter < max_epochs): cprev = c # Alpha times the partial deriviative is our updated # 先求導, 導數相當于步長 update0 = alpha * partial_cost_theta0(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) update1 = alpha * partial_cost_theta1(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) update2 = alpha * partial_cost_theta2(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) update3 = alpha * partial_cost_theta3(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) update4 = alpha * partial_cost_theta4(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) # Update theta0 and theta1 at the same time # We want to compute the slopes at the same set of hypothesised parameters # so we update after finding the partial derivatives # -= 梯度下降,+=梯度上升 theta0 -= update0 theta1 -= update1 theta2 -= update2 theta3 -= update3 theta4 -= update4 # Store thetas theta0s.append(theta0) theta1s.append(theta1) theta2s.append(theta2) theta3s.append(theta3) theta4s.append(theta4) # Compute the new cost # 當前迭代之后,參數發生更新 c = cost(theta0, theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, x1, x2, x3, x4, y) # Store updates,可以進行保存當前代價值 costs.append(c) counter += 1 # Count # 將當前的theta0, theta1, costs值都返回去 #return {’theta0’: theta0, ’theta1’: theta1, ’theta2’: theta2, ’theta3’: theta3, ’theta4’: theta4, 'costs': costs} return {’costs’:costs}print('costs =', gradient_descent(pga.AT, pga.V,pga.AP,pga.RH,pga.PE)[’costs’])descend = gradient_descent(pga.AT, pga.V,pga.AP,pga.RH,pga.PE, alpha=.01)plt.scatter(range(len(descend['costs'])), descend['costs'])plt.show()
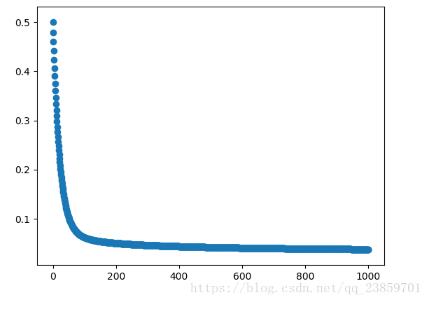
損失函數隨迭代次數變換圖:
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網。
相關文章:

 網公網安備
網公網安備