python實現數字華容道
制作Python數字華容道(可選擇關卡),供大家參考,具體內容如下
由于比賽需要,我這邊制作了一份數字華容道,內含有3,4,5階的數字華容道,開頭在殼窗口內選擇,運用了隨機數模塊(random)和圖形化用戶界面(tkinter)
下面是程序完整代碼
# coding:utf-8 #'''#============================================================作者:@Qss2021年3月20日起草2021年3月21日完工2021年3月23日一次優化完成2021年3月31日完成二次優化(關卡設計)二次優化待解決漏洞:設計關卡后窗口不能自動顯示,需手動切換2021年4月1日三次優化完成,成功解決二次優化bug#============================================================'''from random import * #導入隨機數模塊from tkinter import * #導入圖形化用戶界面模塊step_number = 0 #設置步數的變量,初始值為0difficulty = int(input(’請輸入數字華容道列數(3/4/5):’))def Button_Click_1(x,y): #按鈕點擊事件函數'''聲明空白按鈕行列號和步數的變量為全局變量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判斷判斷點擊按鈕旁是否為空白按鈕,是則交換位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #將步數賦值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步數:’ + str(step_number) #將步數變量導入label控件 '''交換按鈕位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(3):for col in range(3): '''對比所有按鈕序列是否正確,不正確則跳出函數''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按鈕判斷完畢贏得游戲勝利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你贏了’def Button_Click_2(x,y): #按鈕點擊事件函數'''聲明空白按鈕行列號和步數的變量為全局變量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判斷判斷點擊按鈕旁是否為空白按鈕,是則交換位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #將步數賦值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步數:’ + str(step_number) #將步數變量導入label控件 '''交換按鈕位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(4):for col in range(4): '''對比所有按鈕序列是否正確,不正確則跳出函數''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按鈕判斷完畢贏得游戲勝利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你贏了’def Button_Click_3(x,y): #按鈕點擊事件函數'''聲明空白按鈕行列號和步數的變量為全局變量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判斷判斷點擊按鈕旁是否為空白按鈕,是則交換位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #將步數賦值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步數:’ + str(step_number) #將步數變量導入label控件 '''交換按鈕位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(5):for col in range(5): '''對比所有按鈕序列是否正確,不正確則跳出函數''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按鈕判斷完畢贏得游戲勝利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你贏了’'''創建華容道游戲窗口'''root = Tk() #創建圖形化用戶界面實例root.title(’數字華容道’) #設置窗口標題root.geometry('400x400') #將窗口大小設為高400寬400root.configure(bg = ’black’) #將窗口背景設為黑色root.resizable(width = False,height = False) #設置窗口為不可拉伸'''設置歡迎語的label控件'''label_welcomes = Label(root,text = ’歡迎來到數字華容道’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’red’,font = ('Arial',13)) #設置label控件的屬性label_welcomes.place(x = 20,y = 10,width = 250,height = 40) #設置label控件位置'''設置顯示操作方式的label控件'''label_operation = Label(root,text = ’單擊數字’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation.place(x = 3,y = 40,width = 50,height = 30)label_operation_2 = Label(root,text = ’移動方塊’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation_2.place(x = 3,y = 60,width = 50,height = 30)'''設置顯示步數的label控件'''label_step_number = Label(root,text = ’步數:’ + str(step_number),bg = ’black’,fg = ’yellow’,font = ('Arial',10))label_step_number.place(x = 3,y = 20,width = 50,height = 30)if difficulty == 3: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的行號 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的列號 buttons = {} #存放數字按鈕的數組 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’ ’] #所有數字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打亂數字列表中的數字順序 '''制造數字華容道方陣''' for row in range(3): for col in range(3): '''創建數字按鈕,并將行列號傳入該按鈕的點擊事件函數''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_1(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #將按鈕導入數組 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #設置按鈕上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #設置數字按鈕大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判斷是否為空白按鈕,如果是,則記錄到空白按鈕行列號變量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’ ’] #還原數字列表 root.mainloop() #顯示窗口elif difficulty == 4: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的行號 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的列號 buttons = {} #存放數字按鈕的數組 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’ ’] #所有數字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打亂數字列表中的數字順序 '''制造數字華容道方陣''' for row in range(4): for col in range(4): '''創建數字按鈕,并將行列號傳入該按鈕的點擊事件函數''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_2(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #將按鈕導入數組 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #設置按鈕上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #設置數字按鈕大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判斷是否為空白按鈕,如果是,則記錄到空白按鈕行列號變量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’ ’] #還原數字列表 root.mainloop() #顯示窗口elif difficulty == 5: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的行號 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按鈕的列號 buttons = {} #存放數字按鈕的數組 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’16’,’17’,’18’,’19’,’20’,’21’,’22’,’23’,’24’,’ ’] #所有數字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打亂數字列表中的數字順序 for row in range(5): for col in range(5): '''創建數字按鈕,并將行列號傳入該按鈕的點擊事件函數''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_3(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #將按鈕導入數組 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #設置按鈕上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #設置數字按鈕大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判斷是否為空白按鈕,如果是,則記錄到空白按鈕行列號變量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’16’,’17’,’18’,’19’,’20’,’21’,’22’,’23’,’24’,’ ’] #還原數字列表 root.mainloop() #顯示窗口else: print(’未完成此類關卡’)
下面是程序運行結果
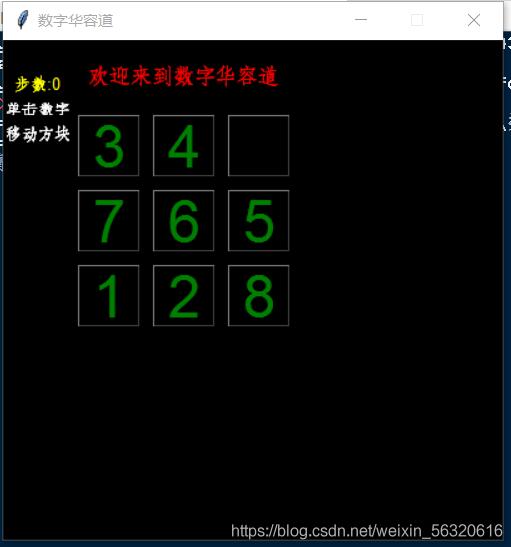
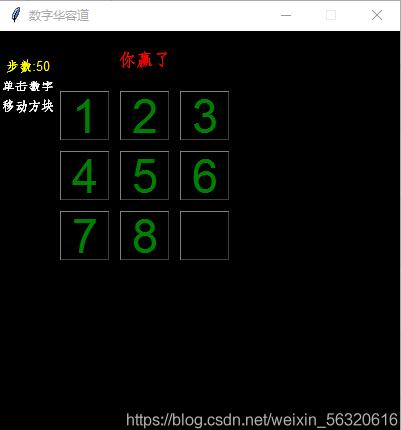
三階華容道加勝利
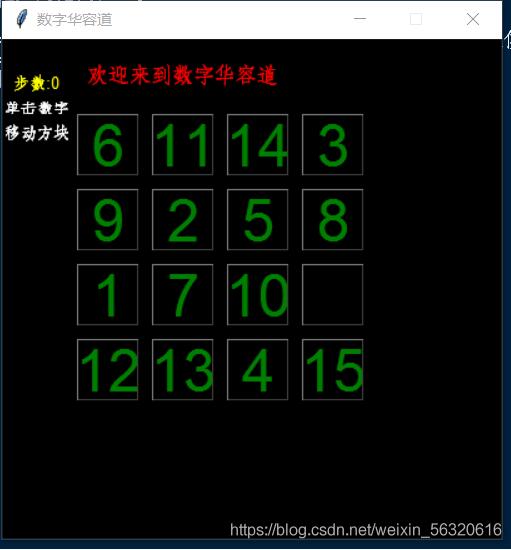
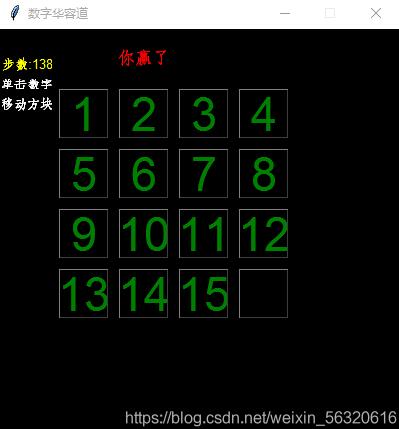
四階華容道加勝利
五階就不傳了,都一樣
接下來說一下代碼原理
首先看下這一段
def Button_Click_1(x,y): #按鈕點擊事件函數'''聲明空白按鈕行列號和步數的變量為全局變量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判斷判斷點擊按鈕旁是否為空白按鈕,是則交換位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #將步數賦值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步數:’ + str(step_number) #將步數變量導入label控件 '''交換按鈕位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(3):for col in range(3): '''對比所有按鈕序列是否正確,不正確則跳出函數''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按鈕判斷完畢贏得游戲勝利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你贏了’
這段是自定義了三個按鈕的點擊事件函數,不過三個都差不多,就是range后面的數字換了(應對不同的階級)。這個函數在注釋上已經寫明了,是判斷點擊按鈕旁是否有空白按鈕的,有則交換位置。后面運用循環嵌套對比序列中的數字和矩陣上的是否一一對應,不對應就跳出循環,對應則判定為贏得游戲。
'''創建華容道游戲窗口'''root = Tk() #創建圖形化用戶界面實例root.title(’數字華容道’) #設置窗口標題root.geometry('400x400') #將窗口大小設為高300寬300root.configure(bg = ’black’) #將窗口背景設為黑色root.resizable(width = False,height = False) #設置窗口為不可拉伸'''設置歡迎語的label控件'''label_welcomes = Label(root,text = ’歡迎來到數字華容道’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’red’,font = ('Arial',13)) #設置label控件的屬性label_welcomes.place(x = 20,y = 10,width = 250,height = 40) #設置label控件位置'''設置顯示操作方式的label控件'''label_operation = Label(root,text = ’單擊數字’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation.place(x = 3,y = 40,width = 50,height = 30)label_operation_2 = Label(root,text = ’移動方塊’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation_2.place(x = 3,y = 60,width = 50,height = 30)'''設置顯示步數的label控件'''label_step_number = Label(root,text = ’步數:’ + str(step_number),bg = ’black’,fg = ’yellow’,font = ('Arial',10))label_step_number.place(x = 3,y = 20,width = 50,height = 30)
這一段創建了圖形化用戶界面,具體每行代碼做什么用的注釋上我都標清楚了。
接著說一下,由于時間有限,只做了在殼窗口內選擇幾階級數字華容道的版本。是用輸入數字來判定的。其他的都是些簡單玩意,比如說按鈕創建,調用函數和循環嵌套,代碼的注釋上都寫了一些大概意思,有點tkinter基礎的應該都能看懂,不會的可以問我。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網。
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備